BSPT Meaning
BSPT Thread (British Standard Pipe Taper Thread)
Full name: British Standard Pipe Taper thread
Standard: Follows BS 21/ISO 7-1 standard.
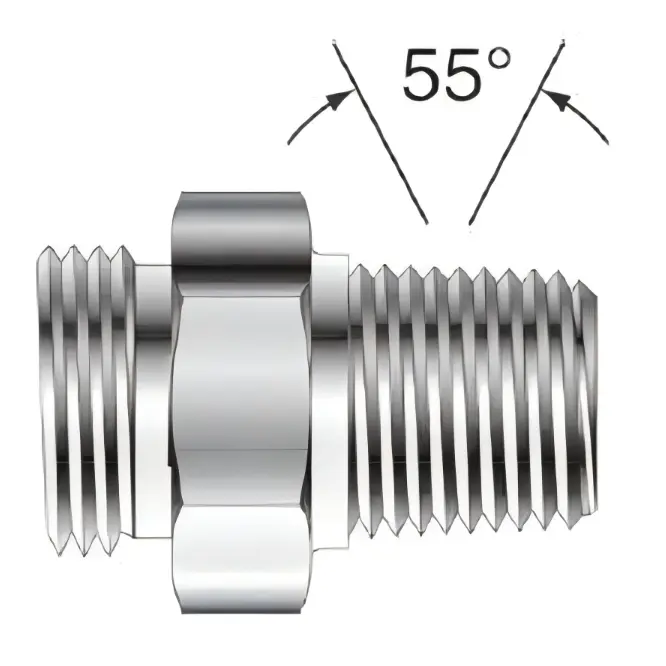
Characteristics: with a 1:16 taper (i.e., 1/16 inch diameter change per inch of length), the thread angle is 55 °.
Sealing mechanism: metal-to-metal sealing is achieved by the taper of the thread itself, usually with a sealant or PTFE tape.
BSPP Meaning
BSPP Thread (British Standard Parallel Pipe Thread)
Full name: British Standard Pipe Parallel thread (British Standard Pipe Parallel Thread)
Standard: In accordance with BS 2779/ISO 228-1.
Characteristics: Straight thread without taper, also with 55° thread angle.
Sealing mechanism: requires an additional sealing washer (usually an O-ring or flat washer) on the end face of the fitting to achieve a seal.
BSPT vs BSPP Difference Explained
| Parameter | BSPT (R Series) | BSPP (G Series) |
| Thread Type | Tapered | Parallel |
| Sealing Method | Thread Deformation Seal | Gasket/O-Ring Seal |
| Pressure Rating | Higher (up to 300 bar) | Lower (typically <100 bar) |
| Common Sizes | 1/16“ to 6” | 1/16“ to 6” |
| Teeth per inch | same as BSPP | same as BSPT |
| Marker Example | R1/2 | G1/2 |
Comparison of BSPT vs BSPP Thread Specification and Dimension Table
BSPT Thread Size Chart
| Inch size | Dash size | Thread Size | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 1⁄8 – 28 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 | 11⁄32 | 0.35 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 1⁄4 – 19 | 33⁄64 | 0.52 | 15⁄32 | 0.47 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 3⁄8 – 19 | 21⁄32 | 0.65 | 19⁄32 | 0.60 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 1⁄2 – 14 | 13⁄16 | 0.82 | 3⁄4 | 0.75 |
| 5⁄8 | -10 | 5⁄8 – 14 | 7⁄8 | 0.88 | 13⁄16 | 0.80 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 3⁄4 – 14 | 1 1⁄32 | 1.04 | 31⁄32 | 0.97 |
| 1 | -16 | 1 – 11 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.30 | 1 7⁄32 | 1.22 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 1 1⁄4 – 11 | 1 21⁄32 | 1.65 | 1 9⁄16 | 1.56 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 1 1⁄2 – 11 | 1 7⁄8 | 1.88 | 1 25⁄32 | 1.79 |
| 2 | -32 | 2 – 11 | 2 11⁄32 | 2.35 | 2 1⁄4 | 2.26 |
BSPP Thread Size Chart

| Inch size | Dash size | Thread Size | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 1⁄8 – 28 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 | 11⁄32 | 0.35 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 1⁄4 – 19 | 33⁄64 | 0.52 | 15⁄32 | 0.47 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 3⁄8 – 19 | 21⁄32 | 0.65 | 19⁄32 | 0.60 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 1⁄2 – 14 | 13⁄16 | 0.82 | 3⁄4 | 0.75 |
| 5⁄8 | -10 | 5⁄8 – 14 | 7⁄8 | 0.88 | 13⁄16 | 0.80 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 3⁄4 – 14 | 1 1⁄32 | 1.04 | 31⁄32 | 0.97 |
| 1 | -16 | 1 – 11 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.30 | 1 7⁄32 | 1.22 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 1 1⁄4 – 11 | 1 21⁄32 | 1.65 | 1 9⁄16 | 1.56 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 1 1⁄2 – 11 | 1 7⁄8 | 1.88 | 1 25⁄32 | 1.79 |
| 2 | -32 | 2 – 11 | 2 11⁄32 | 2.35 | 2 1⁄4 | 2.26 |
Note: Although the dimensional parameters are the same, due to the taper of the BSPT, the actual measurement of the diameter will vary with the position of the
BSPT vs BSPP difference identification method
BSPT vs BSPP Appearance
- Observe the taper:
BSPT: The thread diameter increases gradually from the end to the inside.
BSPP: Thread diameter remains the same, no change. - Thread marking:
BSPT is usually marked with “R” (e.g. R1/2″) or ‘PT’.
BSPP is usually marked with “G” (e.g. G1/2″) or ‘PS’. - Measuring method:
Use calipers to measure the thread diameter at different positions, if there is a significant change, it is BSPP.
Use thread gauge to check taper
BSPT vs BSPP function difference
- Sealing method:
BSPT: The thread itself provides sealing
BSPP: additional seals are required - Mating method:
BSPT usually fits with BSPT or BSPP (the latter requires a gasket).
BSPP usually mates with BSPP and must be gasketed.
BSPT vs BSPP Usage
Typical applications for BSPT
High pressure hydraulic systems
Gas piping systems
Where metal-to-metal sealing is required
High temperature applications (due to lack of elastic seals)
Petrochemical and energy industry piping connections
Typical applications for BSPP
Low pressure hydraulic systems
Water treatment systems
Connections requiring frequent disassembly
Food and pharmaceutical industry (easy cleaning)
Pneumatic systems
BSPT vs BSPP Compatibility Analysis
BSPT vs BSPP Intermating possibilities
BSPT male thread with BSPP female thread:
Can be mated, but gasket required
Not recommended for high pressure applications
BSPP male vs BSPT female:
Theoretically possible, but sealing is not reliable
Should be avoided in practice
BSPT vs BSPPSame type fit:
BSPT-BSPT: optimal sealing performance
BSPP-BSPP: gasket must be used
Compatibility with other thread standards
Incompatible with NPT threads (although both are tapered threads, the angle and pitch are different)
Completely incompatible with metric threads
BSPT vs BSPP Sealing Mechanism Explained
BSPT sealing principle
Taper fit: as the thread is tightened, radial pressure is generated on the taper surface.
Metal deformation: the appropriate amount of surplus leads to a slight metal deformation to achieve sealing
Secondary sealing: Usually requires thread sealant or PTFE tape to fill microscopic gaps.
BSPP Sealing Principle
Face sealing: relies on compression of the joint face and gasket
Sealing element:
O-Ring: elastic seal, suitable for a wide range of media.
Flat gasket: usually metal or composite material
Compression control: the key parameter, too small will leak, too large will damage the seal
BSPT vs BSPP Installation Methods Comparison
BSPT Installation Procedure
- Clean the thread surface
- Wrap PTFE tape around the male threads (clockwise, 2-3 layers).
- Apply appropriate amount of thread sealant (optional)
- Screw in manually until tight to the touch.
- Use tool for final tightening 1-2 turns (avoid over-tightening)
- Pressure test
BSPP Installation Procedure
- Check gasket condition (replace damaged gasket)
- Clean the connection surface
- Place the gasket correctly (O-ring needs to be in the groove)
- manually align and screw in
- Tighten bolts/nuts evenly (if any)
- Tighten flanged connections progressively in diagonal order.
BSPT vs BSPP Installation Precautions
BSPT: Avoid over-tightening which may distort the threads.
BSPP: Ensure that the gasket is properly seated.
Both: Prohibit the use of raw tape as the only means of sealing BSPP.
BSPT vs BSPP Selection Basis and Advantages and Disadvantages Analysis
Pressure Rating:
High pressure: BSPT preferred
Low pressure: BSPP is more economical
Media Characteristics:
Corrosive media: BSPT more reliable
High cleaning requirements: BSPP easier to maintain
Temperature conditions:
High temperature: BSPT (without elastic seals)
Normal temperature: both can be
Vibration environment:
High vibration: BSPT more resistant to loosening
Stable environment: both
Advantages and disadvantages of BSPT vs BSPP
BSPT Advantages:
Higher pressure tolerance
Better temperature resistance
No additional seals required
More resistant to vibration loosening
BSPT Disadvantages:
May require re-threading after disassembly
Higher installation requirements (tightness control)
Not suitable for frequent disassembly
BSPP Advantages:
Easy to install
Easy to disassemble for maintenance
Replaceable gaskets
Face seals are more reliable for low pressure applications
BSPP Disadvantages:
Seal deterioration problems
Lower pressure limits
Additional sealing elements required
BSPT vs BSPP Common Problems and Solutions
BSPT Common Problems
- Leakage problems:
Cause: Inadequate fastening, thread damage, insufficient sealant.
Solution: Reinstall and repair threads if necessary. - Seized threads:
Cause: Over-tightening, poor metal compatibility
Prevention: Use anti-seize lubricant, avoid over-torque. - Difficulty in installation:
Cause: Taper mismatch, thread damage
Inspection: Verify specifications with a thread gauge
BSPP Common Problems
- Gasket failure:
Reason: incompatible materials, excessive compression
Solution: Choose the right material for the gasket and control the compression amount. - End face damage:
Reason: over-tightening, surface roughness
Prevention: Use torque wrenches to ensure the smoothness of the end face. - Wrong installation:
Common mistake: trying to use raw material tape instead of gasket sealing
Correction: Use the specified seals in strict accordance with the requirements
BSPT vs BSPP Common Problems
- Misidentification of thread type:
Consequence: Misfit leads to leakage
Prevention: Clear marking system, train personnel to recognize - Corrosion problem:
Countermeasure: choose the right material according to the medium (e.g. 316 stainless steel) - Maintenance problems:
Suggestion: establish a regular inspection system, especially vibration environment
BSPT vs BSPP Industry Application Trends
- High-pressure field: BSPT is still dominant, but ferrule fittings are gradually replaced
- food and medicine: BSPP’s hygienic design is more popular
- pneumatic system: BSPP is dominant, with the development of quick coupling
- Energy industry: BSPT is still the standard choice for high-pressure pipelines.
See also: jic vs npt vs bsp thread differences
Conclusion:
The correct selection and use of BSPT/BSPP threads is critical to system reliability, taking into account factors such as pressure, media, temperature and maintenance requirements. In practical applications, it is recommended to establish a clear labeling system and installation specifications to ensure connection reliability and reduce the failure rate, if you have other related questions about BSPT vs BSPP you can consult our technical engineers, they will answer your questions for free.





