The entire article is a detailed comparative analysis of NPT and NPS threads, covering definitions, characteristics, uses, differences and key issues in practical applications:
Meaning and characteristics of NPT and NPS threads
NPT (National Pipe Taper) Thread Meaning:
U.S. standard tapered pipe threads with a taper (1:16), thread diameter decreases from inlet to end, sealing is achieved through thread deformation.
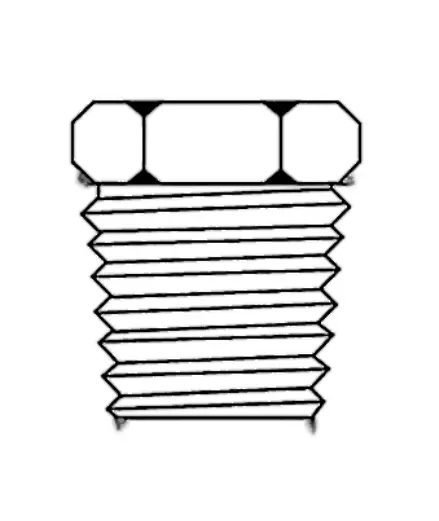
NPT (National Pipe Taper) Thread Features:
Thread angle 60°, both male and female threads are tapered.
Sealing depends on the extruded deformation of the threads as they snap together, usually with a sealant (e.g., tape, thread adhesive).
Conforms to ASME B1.20.1.
NPS (National Pipe Straight) thread meaning:
U.S. standard straight pipe threads, no taper, consistent thread diameter, sealing requires external components.
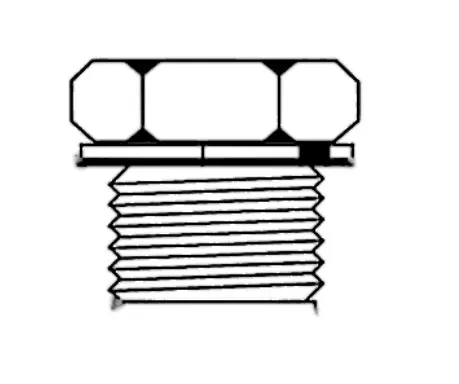
NPS (National Pipe Straight) thread characteristics:
Thread angle 60 °, internal and external threads are cylindrical.
No sealing capability of its own, with gaskets, O-rings or flanges.
Conforms to ASME B1.20.1. Common types include NPSM (for mechanical connections) and NPSF (for fuel systems).
NPT Thread Dimensions
| Nominal Thread Size (inch) | Major diameter (mm) | Major diameter (inch) | TPI (in-1) |
| 1/16 | 7.950 | 0.31 | 27 |
| 1/8 | 10.287 | 0.405 | 27 |
| 1/4 | 13.716 | 0.54 | 18 |
| 3/8 | 17.145 | 0.675 | 18 |
| 1/2 | 21.336 | 0.84 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 26.670 | 1.05 | 14 |
| 1 | 33.401 | 1.315 | 11.5 |
| 2 | 60.325 | 2.375 | 11.5 |
NPS Thread Dimensions
| Pipe Size(inches) | TPI | Pipe diameter(inches) | Pipe diameter(mm) | Female Thread Inside Diameter(inches) | Female Thread Inside Diameter(mm) |
| 1/8 | 27 | 0.405 | 10.3 | 0.34 | 8.636 |
| 1/4 | 18 | 0.540 | 13.7 | 0.47 | 11.94 |
| 3/8 | 18 | 0.675 | 17.1 | 0.59 | 14.98 |
| 1/2 | 14 | 0.840 | 21.33 | 0.75 | 19.05 |
| 3/4 | 14 | 1.050 | 26.67 | 0.97 | 24.638 |
| 1 | 11.5 | 1.315 | 33.4 | 1.20 | 30.48 |
| 1 1/4 | 11.5 | 1.660 | 42.1 | 1.55 | 39.37 |
| 1 1/2 | 11.5 | 1.900 | 48.3 | 1.79 | 45.46 |
| 2 | 11.5 | 2.375 | 60.325 | 2.26 | 57.4 |
| 2 1/2 | 8 | 2.875 | 73.025 | 2.71 | 68.83 |
| 3 | 8 | 3.500 | 88.9 | 3.33 | 84.58 |
| 3 1/2 | 8 | 4.000 | 101.6 | ||
| 4 | 8 | 4.500 | 114.3 | ||
| 4 1/2 | 8 | 5.000 | 127 | ||
| 5 | 8 | 5.563 | 141.3 | ||
| 6 | 8 | 6.625 | 168.275 |
Comparison of NPT VS NPS Core Applications
| Thread Types | Typical Applications | Examples of Applications |
| NPT | High Pressure Fluid Piping, Airtight Systems | Water, Gas, Hydraulic, Fire Protection |
| NPS | Mechanical connections, components to be disassembled for maintenance, use with seals | Structural supports, instrumentation, flanged valve connections |
NPT VS NPS Key Differences and Compatibility
| Comparison Dimensions | NPT | NPS |
| Thread Form | Tapered (1:16 Taper) | Straight (No Taper) |
| Sealing Mechanism | Thread Deformation + Sealant | Gasket/O-Ring/Flange Dependent |
| Removability | Sealing degradation after multiple disassembly | Repeatable disassembly, sealing elements can be replaced |
| Compatibility | Not for direct mixing with NPS, leakage due to mismatch between tapered and straight | Compatible with same type of NPS threads only |
NPT VS NPS Sealing Mechanism
NPT Sealing:
Tapered design allows the internal and external threads to generate radial pressure when tightened, squeezing the sealant to fill microscopic gaps. Suitable for medium to high pressure systems, but over-tightening may result in thread damage.
NPS Seal:
Straight threads are not self-sealing and require a barrier formed by end-face compression gaskets or flanges. Commonly used for low pressure or static connections such as instrumentation installations.
NPT VS NPS Installation Methods and Precautions
NPT Installation Procedure
Clean the threads to remove burrs and oil.
Wrap raw tape (or apply thread adhesive) clockwise along the male threads.
Manually screw in the female threads to avoid misclamping.
Tighten 12 turns with a wrench until resistance is apparent (do not over-tighten).
NPS Installation Procedure
Ensure threads are aligned with sealing groove (e.g. flange, gasket groove).
Place sealing element (gasket/O-ring).
Tighten bolts evenly and compress seals to recommended torque.
NPT VS NPS Advantages and Disadvantages Analysis
| Thread Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| NPT | Self-sealing, suitable for high pressure, low cost | Sealing degradation after disassembly, requires sealant, easily damaged by over-tightening |
| NPS | Reusable, easy to maintain, compatible with a wide range of sealing solutions | Additional seals required, not suitable for high pressure dynamic systems |
How to choose between NPT and NPS threads?
Depending on sealing needs:
High pressure / permanent sealing → NPT.
Low pressure/frequent disassembly → NPS + gasket. Media type:
Gases/corrosive fluids → NPT (reduces risk of leakage).
Static fluids / low temperature systems → NPS. Industry norms:
Petroleum, chemical, fire fighting → NPT is mandatory.
Mechanical manufacturing, instrumentation → NPS is commonly used. Common problems and solutions in the use of NPT VS NPS
Thread leakage
Reason: NPT does not use sealant; NPS gasket aging.
Solution: NPT replenish raw material tape; NPS replace gasket. Seized or damaged threads
Cause: NPT over-tightened; threads not aligned for forced installation.
Solution: Use anti-seize agent; replace fittings. Confusing NPT and NPS
Identify: Observe taper (NPT end is thinner); measure thread diameter (NPT inlet/end sizes are different). High pressure system leakage
Cause: Misuse of NPS straight thread.
Solution: Replace with NPT or use NPS + flange to strengthen the seal. NPT VS NPS Summary
NPT is a tapered sealing thread, suitable for high pressure leak prevention scenarios, but relies on installation skills.
NPS is a straight connecting thread that needs to be matched with a seal and is suitable for removable low pressure systems.
The core of the choice: prioritize sealing needs, media pressure and maintenance frequency.
Key no-no: Never mix NPT and NPS to avoid the risk of system failure.
Understanding the differences and following industry specifications can help you significantly improve the safety and reliability of your piping systems.
By correctly identifying NPT and NPS thread types, following installation procedures and regular maintenance, the risk of leaks and failures can be significantly reduced, and if you have any additional questions about NPT or NPS, contact our engineers first and we’ll answer them for free.





