JIC and SAE Hydraulic Fittings are two of the most commonly used connection fittings in hydraulic system design, but many engineers are confused about their core differences. This article will help you make the best choice with different comparison dimensions and real selection cases.
JIC Standard Meaning (Joint Industry Council)
- Standard Definition
Developed by the United States Joint Industry Council hydraulic joint standard
Current standard: SAE J514 (replacing the earlier JIC specification)
Core features:
37° tapered metal seal (no elastomer)
Thread Type: UN/UNF Unified Threads
Typical markings: JIC06 (3/8“), JIC08 (1/2”) - Key parameters
Taper angle specification requirements: 37° ± 0.5°
Surface roughness specification: Ra ≤ 0.8μm
Pressure rating Specification: 30005000 PSI (carbon steel material)
Applicable temperature: 40℃ ~ 120℃ - Typical applications
Construction machinery (excavator / loader hydraulic lines)
Agricultural equipment (tractor hydraulic system)
Advantage: simple structure, strong resistance to mechanical shock
SAE Standard Meaning (Society of Automotive Engineers)
- Standard definition
A series of specifications developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers
Main joint types:
SAE J1926 (ORFS): O-Ring Flat Seal
SAE J1453 (ORing Boss): Threaded Port Seal
SAE J516: Other Hydraulic Fitting Standards - Core features of ORFS couplings
Sealing method Specification: Flat flange + O-ring (AS568 standard)
O-ring compression rate specification: 1525%.
Pressure rating Specification: 50006000 PSI
Vibration resistance: 35 times better than JIC. - Typical Applications
Automotive brake systems
Aerospace hydraulic lines
Advantage: Zero leakage, suitable for high frequency vibration environments.
JIC vs SAE Hydraulic Fittings Sealing Principle: Structure Determines Performance
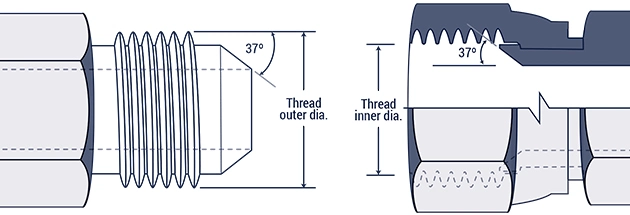
- JIC Hydraulic Fittings (37° taper seal)
Sealing method: metal-to-metal 37° taper press fit
Standard: SAE J514
Characteristics:
Dependent on precise taper machining accuracy (surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.8 μm)
No elastic seal, sealing by metal deformation
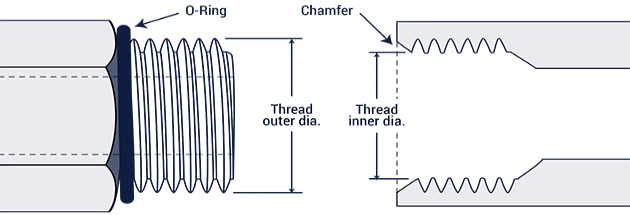
Typical applications: hydraulic lines of construction machinery - SAE O-Ring Hydraulic Fittings (ORFS)
Sealing method: flat flange + O-ring compression
Standard basis: SAE J1926
Features:
O-ring provides elastic compensation (recommended hardness 7090 Shore A)
Flange face must be flat (flatness ≤ 0.02mm)
Typical applications: High pressure and leakage prevention applications.
SAE-J1926-1-and-ISO-11296-1
JIC Hydraulic Fittings Size Chart (SAE J514)
| Inch size | Dash size | Thread Size | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 5⁄16 – 24 | 5⁄16 | 0.31 | 9⁄32 | 0.27 |
| 3⁄16 | -3 | 3⁄8 – 24 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 | 11⁄32 | 0.34 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 7⁄16 – 20 | 7⁄16 | 0.44 | 13⁄32 | 0.39 |
| 5⁄16 | -5 | 1⁄2 – 20 | 1⁄2 | 0.5 | 15⁄32 | 0.45 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 9⁄16 – 18 | 9⁄16 | 0.56 | 17⁄32 | 0.51 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 3⁄4 – 16 | 3⁄4 | 0.75 | 11⁄16 | 0.69 |
| 5⁄8 | -10 | 7⁄8 – 14 | 7⁄8 | 0.88 | 13⁄16 | 0.81 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 1 1⁄16 – 12 | 11⁄16 | 1.06 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 7⁄8 | -14 | 1 3⁄16 – 12 | 1 3⁄16 | 1.19 | 1 1⁄8 | 1.1 |
| 1 | -16 | 1 5⁄16-12 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.31 | 1 1⁄4 | 1.23 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 1 5⁄8 – 12 | 1 5⁄8 | 1.63 | 1 9⁄16 | 1.54 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 1 7⁄8 – 12 | 1 7⁄8 | 1.88 | 1 13⁄16 | 1.79 |
| 2 | -32 | 2 1⁄2 – 12 | 2 1⁄2 | 2.5 | 2 7⁄16 | 2.42 |
SAE Hydraulic Fitting Size Chart (SAE J1926-1)
| Inch size | Dash size | Thread Size | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 5⁄16 – 24 | 5⁄16 | 0.31 | 9⁄32 | 0.27 |
| 3⁄16 | -3 | 3⁄8 – 24 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 | 11⁄32 | 0.34 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 7⁄16 – 20 | 7⁄16 | 0.44 | 13⁄32 | 0.39 |
| 5⁄16 | -5 | 1⁄2 – 20 | 1⁄2 | 0.5 | 15⁄32 | 0.45 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 9⁄16 – 18 | 9⁄16 | 0.56 | 17⁄32 | 0.51 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 3⁄4 – 16 | 3⁄4 | 0.75 | 11⁄16 | 0.69 |
| 5⁄8 | -10 | 7⁄8 – 14 | 7⁄8 | 0.88 | 13⁄16 | 0.81 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 1 1⁄16 – 12 | 1 1⁄16 | 1.06 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 7⁄8 | -14 | 1 3⁄16 – 12 | 1 3⁄16 | 1.19 | 1 1⁄8 | 1.1 |
| 1 | -16 | 1 5⁄16 – 12 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.31 | 1 1⁄4 | 1.23 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 1 5⁄8 – 12 | 1 5⁄8 | 1.63 | 1 9⁄16 | 1.54 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 1 7⁄8 – 12 | 1 7⁄8 | 1.88 | 1 13⁄16 | 1.79 |
| 2 | -32 | 2 1⁄2 – 12 | 2 1⁄2 | 2.5 | 2 7⁄16 | 2.42 |
JIC vs SAE Hydraulic Fittings 7 Key Comparison Dimensions Table Chart
| Comparison | JIC Fittings | SAE ORFS Fittings | Winning Side |
| Maximum Pressure | 5000 PSI | 6000 PSI | SAE |
| Vibration Resistance | Medium (periodic inspection required) | Excellent (O-ring cushioning) | SAE |
| Installation Difficulty | Simple (torque wrench only) | O-ring installation tool required | JIC |
| Maintenance Costs | Low (no consumables) | Medium (O-ring replacement required) | JIC |
| Temperature Range | 40°C~120°C | 50°C~200°C (depending on O-Ring) | SAE |
| Price Comparison | $15$50 | $25$80 | JIC |
| Industry Preferences | 95% adopted by construction machinery | 80% adopted by automotive industry |
JIC vs SAE Hydraulic Fittings Common Misconceptions Clarified
- Naming confusion:
The JIC standard has now been incorporated into SAE J514, but the industry still refers to it as “JIC fittings”.
SAE is a system of standards that includes many types of fittings (ORFS is only one of them). - Interchangeability:
Wrong practice: force to mix JIC and SAE fittings.
Correct solution: use adapters (e.g. Parker 26-6 series conversion kit)
Cost: 15-20% loss of pressure capability after conversion
JIC vs SAE Hydraulic Fittings Frequently Asked Questions
Can I screw a JIC fitting directly into an SAE port?
No, you cannot!
This will cause:
Seal failure (taper will not compress the o-ring)
Thread damage (JIC 37° vs SAE 45°)
Solution: Use an adapter (e.g. Parker 266 series).
Which coupling is better suited for high-pressure pulsating conditions?
SAE ORFS.
Because:
- the O-ring absorbs pressure fluctuations
- the flange construction is more resistant to extrusion
- measured leakage < 0.1 ml/min after 50,000 pulsations
JIC vs SAE Hydraulic Fittings Maintenance Items
| Maintenance Items | JIC Fittings | SAE ORFS Fittings |
| Regular Inspections | Check Taper Wear Every 500 Hours | O-Ring Condition Every 250 Hours |
| |Replacement Criteria | Replacement required if taper depth >0.1mm | Replacement required if O-ring compression set >20% |
| Specialized Tools | Torque Wrench (±5% accuracy) | O-Ring Extractor + Guide Sleeve |
JIC vs SAE Hydraulic Fittings Practical Application Cases
Case 1: Excavator hydraulic system modification
Original configuration: JIC fitting (5000 PSI)
Problem: High-frequency vibration caused the joints to loosen
Retrofit solution: replace with SAE ORFS fittings
Result: 72% reduction in leakage incidents
Case 2: wind power hydraulic system selection
Requirement: 30℃ low temperature environment
Choice: SAE ORFS + Viton O-ring
Reason: Better low-temperature sealing than JIC fittings
How to purchase JIC and SAE Hydraulic Fittings?
Purchasing the right JIC or SAE Hydraulic fittings is a critical step in ensuring optimal performance and safety of your hydraulic system.
Below is your comprehensive guide to purchasing JIC or SAE:
Step 1: Determine your needs:
Determine the specific requirements of your hydraulic system, such as pressure ratings, material compatibility and application type.
Step 2: Find a supplier
Field Authorized Distributors, Internet Web Platforms, Trade Shows and Expositions
Step 3: Confirm the usual questions
Are the fittings certified to meet industry standards?
Warranty period?
Delivery time?
After-sales support?
Step 4: Place an order
Verify all details and place the order.
Step 5: Quality Check
After receiving the product, check the quantity of the product and whether the connector has any defects or discrepancies.
Expert Tips:
1, in corrosive environment, it is recommended to choose SAE 316 stainless steel hydraulic fitting + FFKM O-ring combination, although the price is 3 times of carbon steel JIC, but the service life can be extended 58 times.
2, in the new system, preferred SAE ORFS fittings (especially when the pressure > 3000 PSI), its sealing reliability than the JIC to improve 60%. However, for maintenance of existing JIC systems, it is recommended to keep the standard uniform to minimize compatibility issues.”
— Dr. Robert Langford, Hydraulic Systems Specialist
Conclusion
If you’re not sure what to choose, it’s always wise to consult with one of our hydraulic system experts. We’ll provide you with a free solution, and we’ll provide you with expert advice and high-quality solutions to meet your specific needs for hydraulic fittings.
If you have any further questions or need assistance, please do not hesitate to contact us.
For PDF files or 3D models of specific standards, visit:







