JIC or NPT hydraulic fittings are critical components in hydraulic systems to connect lines, ensure tightness, and transfer high-pressure fluids.JIC (Joint Industry Council) and NPT (National Pipe Tapered) are two widely used standards for hydraulic fittings. This article describes these two types of fittings in detail and compares them in several dimensions. This article will help you to choose the right hydraulic couplings when purchasing.
JIC VS NPT Fittings Standard Meaning
JIC Fittings standard:
JIC (Joint Industry Council) is the American Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) developed standards (SAE J514), mainly used for high-pressure connections in hydraulic systems.
Characteristics: 37 ° conical sealing surface, suitable for high-pressure environment, commonly used in construction machinery, aerospace and industrial equipment.
NPT fitting standard:
NPT (National Pipe Tapered) is an American National Standard (ANSI/ASME B1.20.1), a tapered thread sealing fitting, widely used in piping and low pressure hydraulic systems.
Characteristics: rely on the taper of the threads to achieve sealing, usually need to be used with sealant or raw material tape.
JIC VS NPT Fittings Thread type
JIC fitting thread type:
JIC fittings are usually UN/UNF (Unified Thread), such as UNF (Fine Thread) or UNC (Coarse Thread).
Connection: 37° flare taper seal, no additional sealing material required.
NPT fitting thread type:
NPT is a tapered thread (TPI threads per inch) such as 1/827 NPT (1/8 inch diameter, 27 teeth per inch).
Connection method: relies on the taper of the threads (1°47′) to achieve a seal, which usually requires the use of sealant or raw tape.
JIC VS NPT Fittings Sealing Method
JIC fitting sealing method:
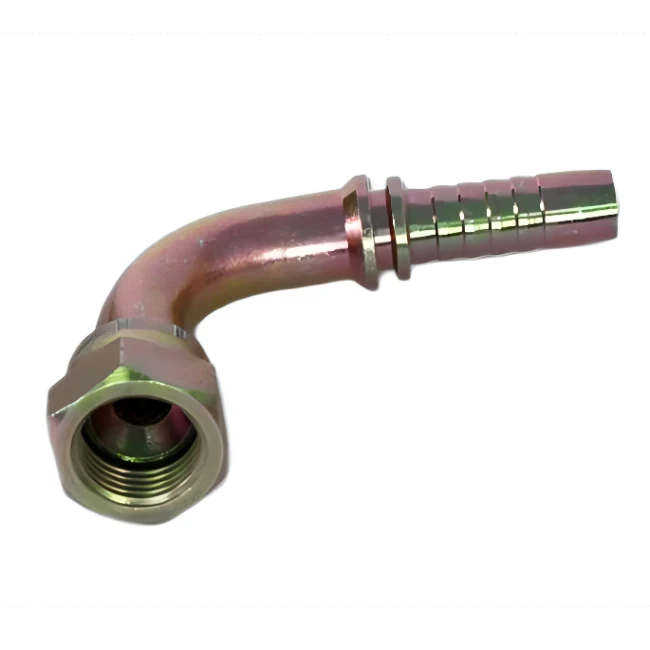

37° metal-to-metal taper sealing, relies on the compression of the fitting and nut to realize the seal, suitable for high-pressure environment.
Advantages: high pressure resistance, vibration resistance, repeatable disassembly.
NPT fitting sealing method:
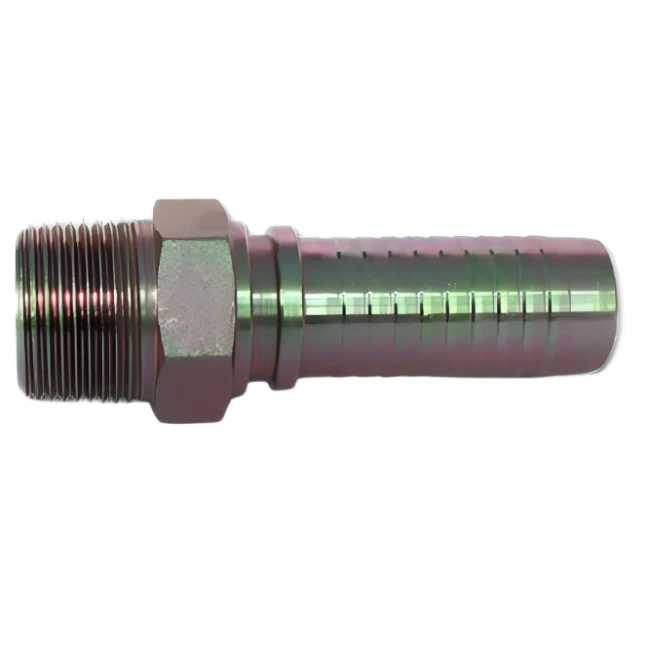

Tapered threads with sealant or raw material tape to achieve sealing, suitable for low and medium pressure systems.
Disadvantages: sealing performance decreases after repeated disassembly, need to reapply sealant.
JIC VS NPT Fitting Pressure Rating
| Fitting Type | Maximum Working Pressure (PSI) | Applicable Scenarios |
| JIC | 3000-6000+ | High Pressure Hydraulic Systems (Construction Machinery, Aerospace) |
| NPT | 1000-3000 | Low-Pressure Hydraulics, Pneumatics, Water Tubes |
JIC VS NPT Dimensional Chart
JIC Fitting Sizes Chart(JIC 37° Flare-SAE J514)
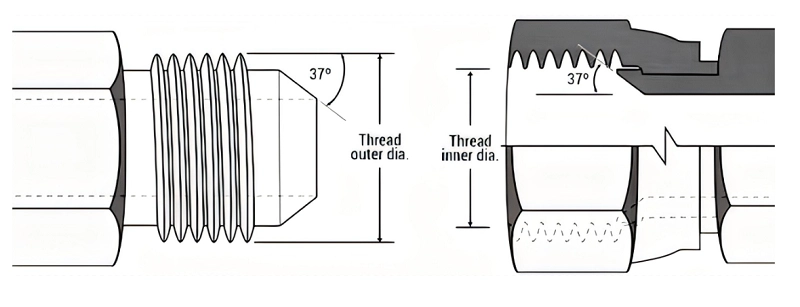
| Inch size | Dash size | Thread Size | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 5⁄16 – 24 | 5⁄16 | 0.31 | 9⁄32 | 0.27 |
| 3⁄16 | -3 | 3⁄8 – 24 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 | 11⁄32 | 0.34 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 7⁄16 – 20 | 7⁄16 | 0.44 | 13⁄32 | 0.39 |
| 5⁄16 | -5 | 1⁄2 – 20 | 1⁄2 | 0.5 | 15⁄32 | 0.45 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 9⁄16 – 18 | 9⁄16 | 0.56 | 17⁄32 | 0.51 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 3⁄4 – 16 | 3⁄4 | 0.75 | 11⁄16 | 0.69 |
| 5⁄8 | -10 | 7⁄8 – 14 | 7⁄8 | 0.88 | 13⁄16 | 0.81 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 1 1⁄16 – 12 | 11⁄16 | 1.06 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 7⁄8 | -14 | 1 3⁄16 – 12 | 1 3⁄16 | 1.19 | 1 1⁄8 | 1.1 |
| 1 | -16 | 1 5⁄16-12 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.31 | 1 1⁄4 | 1.23 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 1 5⁄8 – 12 | 1 5⁄8 | 1.63 | 1 9⁄16 | 1.54 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 1 7⁄8 – 12 | 1 7⁄8 | 1.88 | 1 13⁄16 | 1.79 |
| 2 | -32 | 2 1⁄2 – 12 | 2 1⁄2 | 2.5 | 2 7⁄16 | 2.42 |
NPT Fitting Sizes (NPTF)
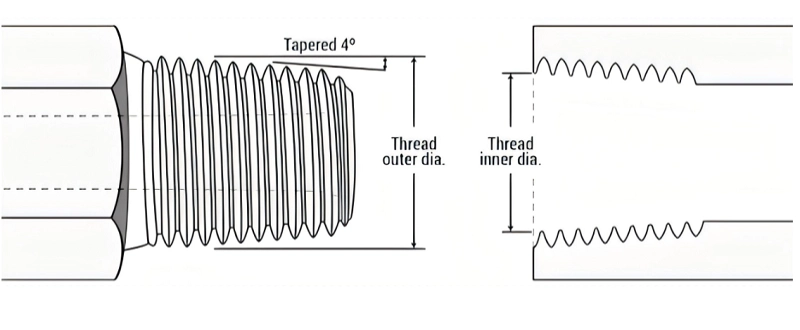
| Inch size | Dash size | Threads per Inch | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 27 | 13⁄32 | 0.41 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 18 | 17⁄32 | 0.54 | 1⁄2 | 0.49 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 18 | 11⁄16 | 0.68 | 5⁄8 | 0.63 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 14 | 27⁄32 | 0.84 | 25⁄32 | 0.77 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 14 | 1 1⁄16 | 1.05 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 1 | -16 | 11 1⁄2 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.32 | 1 1⁄4 | 1.24 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 11 1⁄2 | 1 21⁄32 | 1.66 | 1 19⁄32 | 1.58 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 11 1⁄2 | 1 29⁄32 | 1.9 | 1 13⁄16 | 1.82 |
| 2 | -32 | 11 1⁄2 | 2 3⁄8 | 2.38 | 2 5⁄16 | 2.3 |
Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of JIC vs NPT Fittings
| Comparison Items | JIC Fittings | NPT Fittings |
| Sealing | Metal-to-metal seal, more reliable | Thread dependent seal, prone to leakage |
| Pressure Resistance | Higher (6000+ PSI) | Lower (typically <3000 PSI) |
| Ease of Installation | Special flaring tool required | Wrench and sealant only |
| Reusability | Re-removable for consistent sealing | Re-seal after multiple removals |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
JIC VS NPT Fittings How to choose when purchasing
Pressure requirement: JIC for high pressure system, NPT for low pressure system.
Media type: JIC for hydraulic oil, fuel oil; NPT for water, gas.
Installation environment: vibration occasions (such as construction machinery) preferred JIC.
Budget: NPT cost is lower, but long-term maintenance costs may be higher.
JIC VS NPT Fittings Installation and Maintenance
JIC Fittings Installation
- Use a special flaring tool to make a 37° taper. 2.
- Ensure that the fitting is aligned with the nut to avoid distortion due to over tightening.
- Check sealing surfaces periodically for wear or leakage.
NPT Fitting Installation
- Wrap raw tape around threads or apply sealant.
- Hand tighten and then turn 12 turns with a wrench to avoid over tightening which may cause damage to the threads.
- Check for leaks periodically and reseal as necessary.
JIC VS NPT Fittings Industry Application Scenarios
| Industries | JIC Fittings | NPT Fittings |
| Construction Machinery | ✔ (Excavators, Loaders) | ✖ |
| Aerospace | ✔ (Fuel system) | ✖ |
| Petrochemical | ✔ (High-pressure pipes) | ✔ (Low-pressure pipes) |
| Agricultural machinery | ✔ (Hydraulic systems) | ✔ (Irrigation systems) |
| Water Treatment | ✖ | ✔ (Water pipe connections) |
JIC, NPT Fittings Alternative and Conversion Solutions
JIC to NPT: Use JIC x NPT adapters (e.g. JIC 37° female to NPT male).
NPT to JIC: Also use adapters, but be aware of pressure limitations.
Other alternatives:
ORFS (ORing Face Seal): Higher sealing performance for extreme environments.
BSPP (British parallel thread): European standard, similar to JIC but with a different angle (60°).
JIC VS NPT Fittings Technical Parameters Comparison
| Parameters | JIC | NPT |
| Thread Standard | UN/UNF | NPT (Tapered Thread) |
| Sealing Angle | 37° | 1°47′ (Taper) |
| Pressure Range | 3000-6000+ PSI | 1000-3000+PSI |
| Applicable Temperatures | -65°F to +400°F | -20°F to +250°F |
| Common Sizes | 1/8“ to 2” | 1/16“ to 4” |
JIC VS NPT Hydraulic Fittings Frequently Asked Questions
Which is better, JIC or NPT?
JIC advantage: high pressure resistance, reliable sealing, anti-vibration, suitable for construction machinery, aerospace.
NPT advantage: low cost, simple installation, suitable for water, pneumatic and low pressure hydraulic systems.
Selection basis: according to the pressure, media, budget decision
Can JIC and NPT be connected directly?
Can not be directly connected, need to use the conversion connector (such as JIC female to NPT male thread).
Note: After conversion, the system pressure should not exceed the tolerance range of NPT.
Is it easy to confuse the size of JIC and NPT?
It is easy to confuse them.
For example: 1/2“ JIC ≠ 1/2” NPT (different threads)
1/4“ JIC (UNF thread) is not compatible with 1/4” NPT (NPT thread).
Solution: Use a thread gauge or consult a size comparison chart.
How can I avoid common problems when choosing JIC or NPT Fittings?
- Select the correct type of fitting (JIC for high pressure, NPT for low pressure). 2.
- Use the proper tools for installation (JIC requires a flaring tool, NPT requires raw tape). 3.
- Regular inspection and maintenance to prevent leakage and thread wear. 4.
- Avoid mixing standards (e.g. JIC and NPT are not directly compatible).
Conclusion
JIC fittings are more suitable for high pressure, high vibration environments such as construction machinery and aerospace.
NPT fittings are suitable for low-pressure, low-cost applications such as plumbing and pneumatic systems.
Pressure, sealing, ease of installation and cost need to be considered when choosing.
We hope this article can help you to choose and use JIC and NPT hydraulic fittings correctly, if you still have any questions, please contact our technical staff, we will answer you for free.





