BSP Thread Meaning and Characteristics
BSP thread (British Standard Pipe Thread)
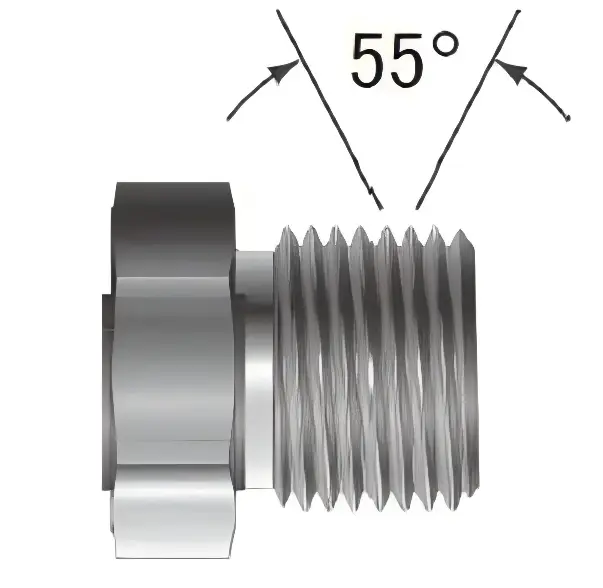
BSPP (G series): parallel thread (cylindrical thread), tooth angle 55 °, rely on gasket or O-ring sealing.
BSPT (R series): conical thread (1:16 taper), tooth angle 55°, sealing by thread deformation.
Standard: ISO 228 (BSPP), ISO 7 (BSPT), widely used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems in Europe and Asia.
Recommended articles for BSP threads: https://hydraulicfittingstypes.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-bspt-thread-vs-bspp-thread/
NPT Thread Meaning and Characteristics
NPT thread (American Standard Tapered Pipe Thread)
Characteristics: Tapered thread (1:16 taper), tooth angle 60°, relies on thread fit and sealant (e.g., biotape) sealing.
Standard: ASME B1.20.1, mainstream in North America, for liquid and gas piping systems.
Recommended articles for NPT threads:
NPT vs NPTF Thread Differences, The Ultimate Guide.
National Pipe Tapered npt vs National Pipe Straight nps
BSP vs NPT Thread Size Chart

BSPP Parallel Thread Size Chart
| Inch size | Dash size | Thread Size | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 1⁄8 – 28 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 | 11⁄32 | 0.35 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 1⁄4 – 19 | 33⁄64 | 0.52 | 15⁄32 | 0.47 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 3⁄8 – 19 | 21⁄32 | 0.65 | 19⁄32 | 0.60 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 1⁄2 – 14 | 13⁄16 | 0.82 | 3⁄4 | 0.75 |
| 5⁄8 | -10 | 5⁄8 – 14 | 7⁄8 | 0.88 | 13⁄16 | 0.80 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 3⁄4 – 14 | 1 1⁄32 | 1.04 | 31⁄32 | 0.97 |
| 1 | -16 | 1 – 11 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.30 | 1 7⁄32 | 1.22 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 1 1⁄4 – 11 | 1 21⁄32 | 1.65 | 1 9⁄16 | 1.56 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 1 1⁄2 – 11 | 1 7⁄8 | 1.88 | 1 25⁄32 | 1.79 |
| 2 | -32 | 2 – 11 | 2 11⁄32 | 2.35 | 2 1⁄4 | 2.26 |
BSPT Tapered Thread Size Chart
| Inch size | Dash size | Thread Size | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 1⁄8 – 28 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 | 11⁄32 | 0.35 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 1⁄4 – 19 | 33⁄64 | 0.52 | 15⁄32 | 0.47 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 3⁄8 – 19 | 21⁄32 | 0.65 | 19⁄32 | 0.60 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 1⁄2 – 14 | 13⁄16 | 0.82 | 3⁄4 | 0.75 |
| 5⁄8 | -10 | 5⁄8 – 14 | 7⁄8 | 0.88 | 13⁄16 | 0.80 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 3⁄4 – 14 | 1 1⁄32 | 1.04 | 31⁄32 | 0.97 |
| 1 | -16 | 1 – 11 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.30 | 1 7⁄32 | 1.22 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 1 1⁄4 – 11 | 1 21⁄32 | 1.65 | 1 9⁄16 | 1.56 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 1 1⁄2 – 11 | 1 7⁄8 | 1.88 | 1 25⁄32 | 1.79 |
| 2 | -32 | 2 – 11 | 2 11⁄32 | 2.35 | 2 1⁄4 | 2.26 |
NPT Thread Size Chart
| Inch size | Dash size | Threads per Inch | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Female thread O.D (in) | ||
| 1⁄8 | -2 | 27 | 13⁄32 | 0.41 | 3⁄8 | 0.38 |
| 1⁄4 | -4 | 18 | 17⁄32 | 0.54 | 1⁄2 | 0.49 |
| 3⁄8 | -6 | 14 | 11⁄16 | 0.68 | 5⁄8 | 0.63 |
| 1⁄2 | -8 | 14 | 27⁄32 | 0.84 | 25⁄32 | 0.77 |
| 3⁄4 | -12 | 14 | 1 1⁄16 | 1.05 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 1 | -16 | 11 1⁄2 | 1 5⁄16 | 1.32 | 1 1⁄4 | 1.24 |
| 1 1⁄4 | -20 | 11 1⁄2 | 1 21⁄32 | 1.66 | 1 19⁄32 | 1.58 |
| 1 1⁄2 | -24 | 11 1⁄2 | 1 29⁄32 | 1.90 | 1 13⁄16 | 1.82 |
| 2 | -32 | 11 1⁄2 | 2 3⁄8 | 2.38 | 2 5⁄16 | 2.30 |
BSPvs NPT thread difference parameters comparison:
| Parameters | BSPP (G series) | BSPT (R series) | NPT |
| Labeling Examples | G1/2, G3/4 | R1/2, R3/4 | 1/2-14 NPT |
| Tooth Angle | 55° | 55° | 60° |
| Taper | None (parallel) | 1:16 | 1:16 |
| Teeth per Inch | 14 (G1/2) | 14 (G1/2) | 14 (1/2 NPT) |
| Sealing Method | Gaskets/O-Rings | Thread Deformation + Sealant | Thread Deformation + Sealant |
How to distinguish BSP vs NPT threads?
- Tooth angle measurement: Use a thread gauge, 55° for BSP, 60° for NPT.
- Thread taper observation: the diameter of conical threads (BSPT/NPT) increases gradually from the end inwards, while the diameter of parallel threads (BSPP) is constant.
- Marking identification: BSP threads are marked with “G” or “R”, NPT is directly marked with “NPT”.
BSP vs NPT threads are they compatible and why?
BSP vs NPT threads critical issues analysis:
Thread angle difference: 55° vs 60°, resulting in a mismatch of thread profiles, which may cause localized stress concentrations and leakage.
Pitch Differences: Some sizes have different pitches (e.g. 3/4“ BSP is 14 TPI and NPT is 14 TPI, but 1/8” BSP is 28 TPI and NPT is 27 TPI).
Taper fit: BSPT and NPT are both 1:16 taper, theoretically tapered threads can be partially fit, but sealing is not reliable.
Differences in BSP vs NPT Thread Sealing Methods
-BSPP (G series): relies on face sealing (gaskets), which conflicts with NPT’s taper sealing principle.
-BSPT (R series): sealing by thread deformation, similar to NPT, but differences in thread angle and tooth shape may result in poor sealing.
-NPT: relies on thread engagement + sealant, may cause leakage due to mismatch of tooth shapes when combined with BSP threads.
Compatibility of BSP vs NPT threads in practical applications
Contingency: In low-pressure, non-critical systems, BSPT vs NPT may be temporarily adapted by raw tape or sealant, but long-term use is risky.
High pressure/critical systems: mixing is prohibited as unreliable sealing may result in leakage or thread damage.
BSP vs NPT Thread Compatibility Solutions
Adapters/transition fittings:
Use a BSP to NPT transition fitting (e.g. BSPP Male to NPT Female).
Select specialty adapters with gaskets or metal sealing surfaces.
Rework threads:
Where permitted, standardize threads at the equipment end (e.g., full conversion to NPT or BSP).
Seal material enhancement:
For low-pressure systems, try filling the thread gap with a highly elastic sealant.
BSP vs NPT Thread Compatibility Summary
| Compatibility Class | Scenarios | Risks |
| Incompatibility | BSPP (G) vs NPT | Parallel threads cannot be sealed effectively with tapered threads |
| Partially Compatible | BSPT (R) with NPT (for emergency use) | Same taper but different thread angle, requires large amounts of sealant, low pressure, non-critical temporary use only. |
| Compatible | Use adapter | Reliable connection via specialized adapter |
Precautions in the use of BSP vs NPT threads
- Avoid forced installation: forcing threads of different standards to be screwed together may result in thread damage or system failure.
- Pressure and media: High temperature, high pressure or corrosive media will magnify the risk of sealing defects.
- Consistency of standards: Thread standards should be standardized at the design stage to reduce the cost of adaptation at a later stage.
BSP vs NPT thread usage
BSP: Commonly used in Europe/Asia hydraulic systems, pneumatic tools, low pressure piping (such as cooling water lines).
NPT: Mainstream choice for North American petroleum, chemical, water supply and drainage systems, especially suitable for medium and high pressure scenarios.
BSP vs NPT thread sealing treatment
BSPP: must be paired with a flat washer or composite seal (e.g. ISO 1179 standard).
BSPT/NPT: Apply sealant or wrap raw material tape (3-4 layers) after thread engagement to avoid excessive clogging of pipes.
BSP vs NPT Thread Installation
BSPP: After hand screwing, use a tool to screw 1/4~1/2 turn to ensure even pressure on the gasket.
BSPT/NPT: After hand screwing to fit, tool to add 1.5~3 turns (NPT need to be tighter), pay attention to avoid excessive lead to cracking.
BSP vs NPT thread selection guide
Geographical factors: Europe choose BSP, North America choose NPT.
Pressure requirements: NPT or BSPT for high pressure, BSPP for low pressure static systems.
Maintenance Frequency: BSPP is preferred for frequent disassembly scenarios (gaskets are easy to replace).
BSP vs NPT Thread Advantages and Disadvantages Analysis
| Types | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| BSPP | Easily disassembled, replaceable seals | Leaks easily at high pressures |
| BSPT | Better sealing than BSPP | Requires rethreading after removal |
| NPT | Good high pressure sealing, common to North America | Over-tightening damages threads, requires precise installation |
BSP vs NPT Thread Common Problems and Solutions
- Leakage problems
Cause: Mis-mixed threads or insufficient sealing.
Solution: Use the correct thread type, NPT/BSPT with sufficient sealant. - Thread seizing
Cause: Over tightening or not using lubricant.
Solution: Apply anti-seize agent (e.g. molybdenum disulfide) and control the number of tightening turns. - System compatibility error
Case: BSP equipment mistakenly connected to the NPT connector resulting in leakage.
Solution: Use transition fittings (e.g. BSP-NPT adapter) and test the pressure.
BSP vs NPT thread difference and compatibility summary
BSP and NPT threads need to be strictly differentiated due to the differences in standard systems. Proper selection requires a combination of geography, pressure, maintenance needs, and adherence to installation specifications to ensure sealing and durability. The proper application of adapters and sealants is critical in cross standardized systems. If you have any other questions about BSP vs NPT threads, please contact our engineers, who will answer them for you free of charge.